RGE Research reports
Renewable Energy
Solar energy is a renewable, clean energy source that does not pollute the environment and does not create carbon emissions. With the gradual increase in population and industrialization, the need for energy in the world is constantly increasing. With the decrease in oil and natural gas resources day by day and in countries that do not have these resources, responding to the increasing need for energy creates a very troublesome situation. Therefore, turning to cleaner and less costly renewable energy sources helps to eliminate this problem.
The first resources that come to mind when we say renewable energy sources are hydro-HPP (water power), wind-WPP, solar-SPP, biomass and geothermal resources.
Electricity Generation from Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is energy that can be obtained from non-fossil natural resources such as sun, wind, hydraulic, geothermal, geothermal, biomass, sea (wave, current and tidal) and can be permanently supplemented by nature. Since renewable energy sources are self-existing, inexhaustible resources that do not deplete over time, alternative energy sources are increasingly being used.
With the gradual increase in population and industrialization, the need for energy in the world is increasing, albeit in a limited way. According to the "Global Energy Perspective 2022" report by the world-renowned consulting firm McKinsey, the world's energy demand is expected to increase by 14% by 2050. On the other hand, electricity consumption is projected to replace the use of fossil fuel products during this period. The main reason for this development is that, as a result of country policies, electricity has reduced carbon dioxide emissions compared to alternatives and is the most cost-effective and simplest way to be used as an energy source in many sectors. In addition to this development, the use of renewable energy in electricity generation is projected to reach 50% by 2035 and 85% by 2050. The main reason for this development is that it is both sustainable and relatively low cost.
According to the International Energy Association (IEA), which was founded by 31 countries, including Turkey, the ratio of electricity generated from renewable energy sources to total electricity generation is estimated to reach 28.7% in 2021, up from 20.2% in 2011. Within the United Nations-led goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions as much as possible to zero by 2050, it is envisaged to increase the ratio of electricity generation from renewable energy sources to total generation to 60% by 2030. Within this target, electricity generation capacity from renewable sources, which reached 340 GW in 2022, should grow by 12% annually until 2030.
Global Electricity Generation Volume and Growth from Renewable Energy Sources (2011-2021)
| Source | 2021 Production Volume (TW) | Production Share (%) | 2011 Production Volume (TW) | 2011-2021 Growth (%) |
| Hydraulic | 4.327,7 | 53,3 | 3.520,1 | 23 |
| Wind | 1.870,3 | 23,0 | 437,3 | 328 |
| Solar | 1.002,9 | 12,4 | 63,8 | 1.472 |
| Bioenergy | 764,2 | 9,4 | 392,0 | 95 |
| Other | 151,0 | 1,9 | 72,7 | 108 |
| Total | 8.116,1 | 100,0 | 4.485,9 | 81 |
Source: https://www.iea.org/reports/renewable-power
As can be seen from the table above, the volume of electricity generation from renewable energy sources has grown by 81% in the last 10 years, reaching 8,116.9 TW in 2021. Although hydropower still accounts for the largest share among renewable energy sources with 53.3%, solar energy has the highest growth rate of 1,472% in this period.
Solar Energy
Electricity Generation with Solar Energy
The radiant energy released by the fusion process (the transformation of hydrogen gas into helium) of the nuclei of hydrogen gas, which makes up about 90 percent of the sun, is called "Solar Energy".
The sun is a clean and inexhaustible source of renewable energy, emitting approximately 3.9x1026 Watts of power. A very small amount of this energy emitted from the sun reaches the Earth as radiation energy. On average, 1,367 W of radiation energy reaches each square meter on the outer surface of the atmosphere. The process of converting this radiation into electrical energy with special panels forms the basis of the sector.
Solar energy is a renewable energy source with features such as ease of installation and use, as well as not polluting the environment, not releasing any gases and not creating harmful waste.
It is not possible to provide the energy needed for industrial, residential or individual use directly and consistently from the sun. For this reason, solar energy can be converted and used in various ways. Many technologies have been developed to utilize the sun's rays. While solar energy technologies vary widely in terms of method, material and technological level, some of them use solar energy directly in the form of light or heat energy, while other technologies are used to generate electricity from solar energy. Direct or indirect electricity generation, hot water production, space heating and cooling, process heat energy for industrial organizations and greenhouse heating are some of the applications of solar energy.
Solar energy technologies are basically divided into two main groups.
1. Heat-related (Thermal) Solar Energy Technologies
Thermal Solar Energy Technologies are divided into two as low temperature applications and concentrating thermal systems according to the temperature values obtained.
1.1. Low Temperature Applications
Applications such as water purification systems, solar architecture, crop drying and greenhouse heating systems and solar cooking, solar collectors, solar pools, solar chimneys are applications for obtaining low temperatures from solar energy. Among these application types, planar solar collectors are the simplest and most common method of utilizing solar energy. Planar solar collectors work on the principle of transmitting solar energy to water, air or another fluid. These systems are mostly used for heating water in homes. The temperature they reach is around 70°C
1.2. Concentrating Thermal Systems
Concentrated thermal solar thermal technologies are mainly used for electricity generation. The installed capacity of generation plants based on these technologies is 10 megawatts or more. In concentrating thermal solar technologies, parabolic mirrors, dishes or heliostats, which are scientific instruments that use a mirror to reflect sunlight in a specific direction, are used as solar concentrators.
2. Photovoltaic Solar Technologies
Solar modules, the most basic component of photovoltaic solar technologies, convert solar energy directly into electrical energy. Solar modules consist of photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity. The word photovoltaic is composed of the words "photon", the fundamental particle that makes up sunlight, and "voltage", the unit of electrical power. Photovoltaic cells are also called Solar Cell and Solar Battery.
The photovoltaic phenomenon, first proposed by the French scientist Edmond Becquerel in 1839, was discovered by the light emission of the electrode in a conductive liquid. In 1877, W. G. Adams and R.E. Day observed the photovoltaic effect in solidified selenium. This was followed by the selenium solar cell developed by C. Fritts in 1883, which was placed on a thin layer of gold and had an efficiency of less than 1%. Following these developments, W. Hallwachs designed a semiconductor junction solar cell using copper and copper oxide. In 1904, A. Einstein's paper on the photoelectric effect from a quantum perspective led to a better understanding of this effect. Starting in 1954 with the first Si p-n junction solar cell produced by Bell Laboratories, the production of electricity from the sun has reached today and has been the subject of great developments and many studies.
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are square, rectangular or circular surfaces with an area of approximately 100 cm⊃2; and a thickness of 0.2-0.4 mm. The most widely used material in photovoltaic solar technologies is the element silicon. Solar modules are formed by combining solar cells together.
In the production of electricity from solar cells; mostly silicon-based solar cells, panels and materials such as glass protecting the panel surfaces, encapsulant, aluminum frames and transparent backsheet are used. The positively and negatively charged parts of the cell create a potential difference for electron movement. This is how light hits the solar cells,
Their electrons are displaced around the atoms of the cells, creating electric current. The resulting direct current (DC) is converted into alternating current (AC) for use by consumers through inverter devices.
Today, the surface area of solar modules used for electricity generation has reached 2.1 m2 and their power has reached 675 WattPeak. The WattPeak value indicates the maximum power that solar panels can produce under optimum conditions at standard temperature and daylight. High-power solar panels and solar power plants (SPPs) can be built by combining solar modules. Depending on today's technologies and the type of installation (fixed system, sun-following systems), a SPP with a capacity of 1 MWe can be installed on an area of 13-25 acres. Especially with SPPs installed on the roofs and facades of buildings, the electricity needed can be generated at consumption points.
Source:https://enerji.gov.tr/bilgi-merkezi-enerji-gunes
Turkey's Solar Energy Potential
Turkey has a significant solar energy potential due to its geographical location. According to the Turkey Solar Energy Potential Atlas (GEPA) prepared by the Turkish Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources, the average annual total sunshine duration is 2,741 hours and the average annual total radiation value is calculated as 1,527.46 kilowatt hours/m2 . The general potential outlook and monthly average global radiation distribution in the GEPA announced by the Ministry are shown in the following figures:
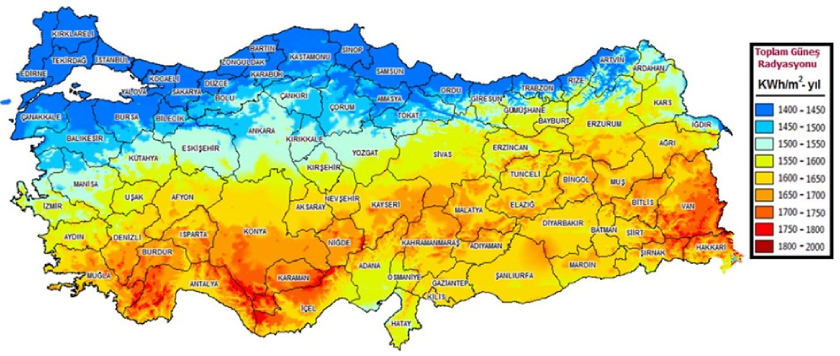
Source: https://enerji.gov.tr/eigm-yenilenebilir-enerji-kaynaklar-gunes
Monthly Average Radiation Value (kWh/m2)
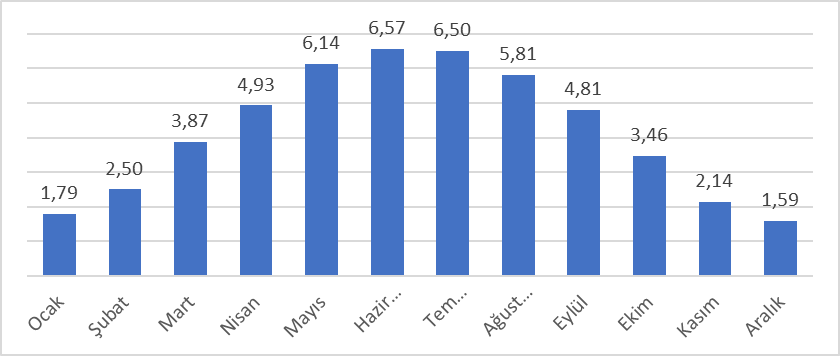
Source: https://enerji.gov.tr/eigm-yenilenebilir-enerji-kaynaklar-gunes
Wind Energy
Electricity Generation with Wind Energy
Wind energy is the kinetic energy of air in motion, caused by differential heating of the earth's surface by solar radiation. The different heating of the earth's surface causes the temperature, humidity and pressure of the air to be different, and this different pressure causes the air to move. About 2% of the solar energy reaching the Earth is converted into wind energy. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy. The rotating blades of wind turbines are connected to an electric generator by means of a shaft. The electric generator converts the rotational motion into electrical energy.
According to Ember, a global independent think tank, about 1,814 TW hours, or about 7.3% of the world's electricity consumption, which is projected to reach about 25,000 TW hours in 2021, is projected to be generated from wind energy. In 2011, this ratio is estimated to be 440 TW hours, which is only 2% of the total generation of 21,640 TW hours.
Turkey's Wind Energy Potential
According to the information obtained from the Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources of the Republic of Turkey, according to the 2006 Turkey Wind Energy Potential Atlas (REPA-V1), it was accepted that a wind power plant with a capacity of 5 MW per square kilometer could be established in usable areas 50 meters above ground level and with annual average wind speeds above 7.5 m/s, and it was determined that the total capacity of wind power plants that could be established in Turkey was 47,849 MW.
Wind Energy Potential Atlas
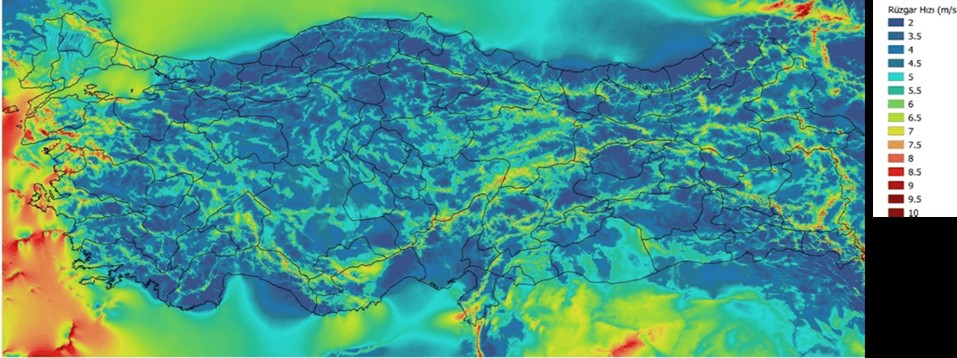
Source: https://enerji.gov.tr/eigm-yenilenebilir-enerji-kaynaklar-ruzgar
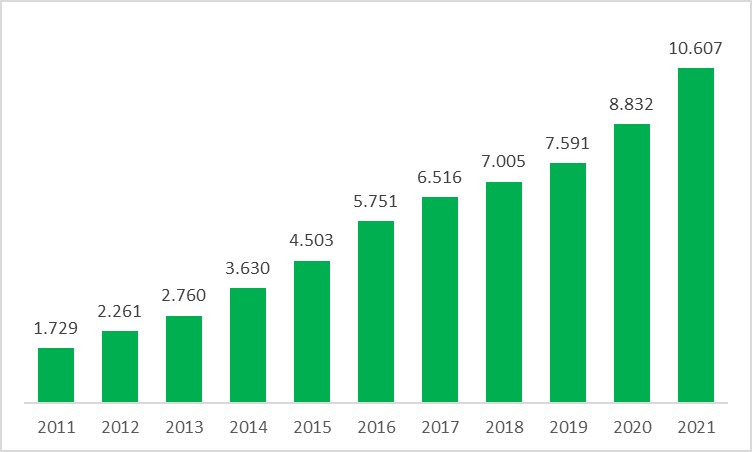
According to EMRA data, the amount of installed capacity based on wind energy in Turkey over the years and the ratio of this amount to the total capacity in Turkey are shown in the following graphs. As can be seen in the graphs, the amount of installed capacity has increased approximately 6.5 times in 11 years from 1,729 MWe in 2011 to 11,199 MWe as of September 2022. This amount corresponds to only 23% of Turkey's wind power capacity as stated in the 2016 report.
Electricity Generation Capacity with Wind Energy in Turkey (MWe)